Vector Analysis
Querying and overlaying vector layers, key operations and techniques.
Vector Analysis
Many operations can be done with vector data.
- Some methods are very similar.
- Distinctions between methods can be subtle, but important.
- Can complete the same tasks, but need slight changes to a workflow.
- Typically in GIS there are multiple ways to get the same answers.
- Some "routes" are just more direct.
Attribute Queries
Finding features of interest based on attributes.
- A good way to reduce data volumes, export queries to new layers.
- In ArcGIS Pro, you can use SQL (Structured Query Language), to Select by Attribute.
- If we're only interested in historic residential buildings:
- Where "YEAR BUILT" <= 1950 AND "TYPE" = "Residential"
- Save as a new layer, won't have to search through all the objects every time.
Select by Attribute
Check equality, relative magnitude, etc.
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine"
- Where "SPECIES" ≠ "Pine"
- Where "HEIGHT" <= 5
| Species | Age | Height |
| Pine | 10 | 5 |
| Pine | 95 | 28 |
| Oak | 200 | 25 |
| Oak | 5 | 4 |
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine"
- Where "SPECIES" ≠ "Pine"
- Where "HEIGHT" <= 5
| Species | Age | Height |
| Pine | 10 | 5 |
| Pine | 95 | 28 |
| Oak | 200 | 25 |
| Oak | 5 | 4 |
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine"
- Where "SPECIES" ≠ "Pine"
- Where "HEIGHT" <= 5
| Species | Age | Height |
| Pine | 10 | 5 |
| Pine | 95 | 28 |
| Oak | 200 | 25 |
| Oak | 5 | 4 |
Select by Attribute
Combined with operators: AND / OR
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine" AND "HEIGHT" <= 5
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine" OR "HEIGHT" <= 5
| Species | Age | Height |
| Pine | 10 | 5 |
| Pine | 95 | 28 |
| Oak | 200 | 25 |
| Oak | 5 | 4 |
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine" AND "HEIGHT" <= 5
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine" OR "HEIGHT" <= 5
| Species | Age | Height |
| Pine | 10 | 5 |
| Pine | 95 | 28 |
| Oak | 200 | 25 |
| Oak | 5 | 4 |
Select by Attribute
Requires careful consideration:
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine" AND "SPECIES" = "Oak"
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine" OR "SPECIES" = "Oak"
| Species | Age | Height |
| Pine | 10 | 5 |
| Pine | 95 | 28 |
| Oak | 200 | 25 |
| Oak | 5 | 4 |
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine" AND "SPECIES" = "Oak"
- Where "SPECIES" = "Pine" OR "SPECIES" = "Oak"
| Species | Age | Height |
| Pine | 10 | 5 |
| Pine | 95 | 28 |
| Oak | 200 | 25 |
| Oak | 5 | 4 |
Proximity Analysis
Looking at spatial relationships within or between layers.
- A good way to reduce data volumes, export queries to new layers.
- Multiple options, depending on our needs.
- If we're only interested in buildings within 1 km of streams:
- Identify by proximity
- Save as a new layer, won't have to search through all the objects every time.
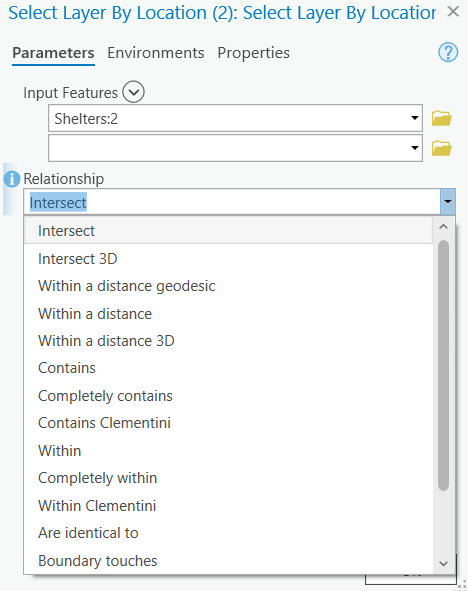
Select by Location
Use Select by Location when you want to check for spatial relationships. There are many relationships we can check for:
- Containment
- Intersection
- Distance
Geometric Manipulations
These methods create new layers with altered "geometries". Geometry is a term we use to refer to points, lines, and/or polygons in a vector layer.
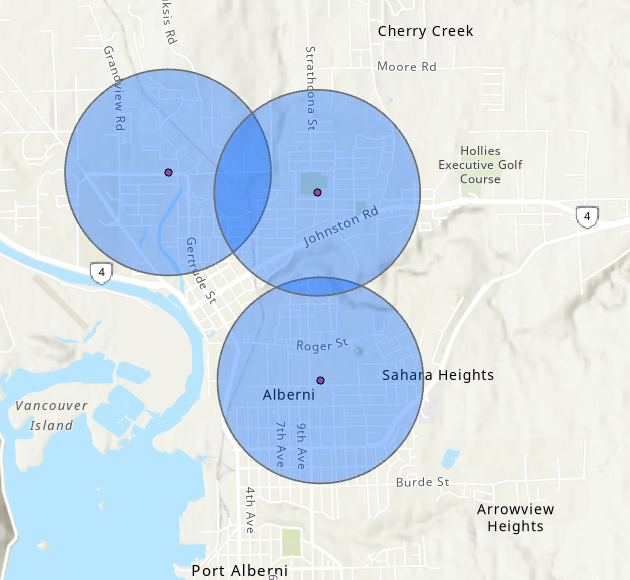
Buffering
Use the Buffer tool to create a new Polygon layer based on distance.
- Buffer points, lines, or polygons using a buffer distance or set a field to specify varriable distance.
- Use the Multiple Ring Buffer tool for multi-criteria buffers.
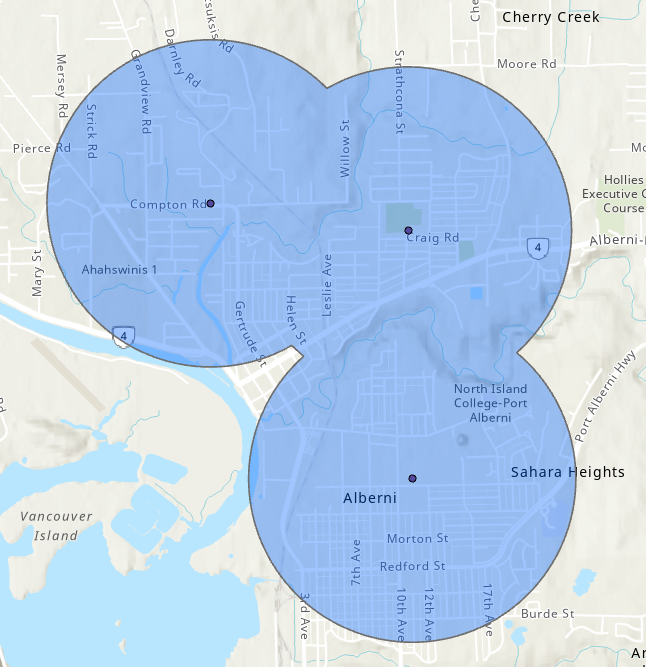
Dissolve
Dissolve aggregates features.
- Merges objects completly or by attribute(s).
- Can calculate statistics for aggregated regions.
- Useful if our data is more "complex" than we need it to be.
Feature Overlay
When we have multiple data layers and we want to combine them to form a new output.
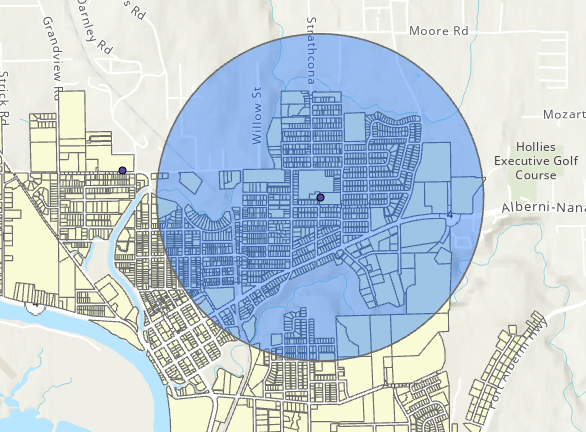
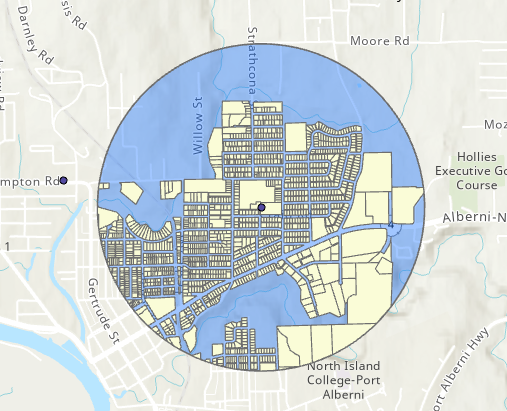
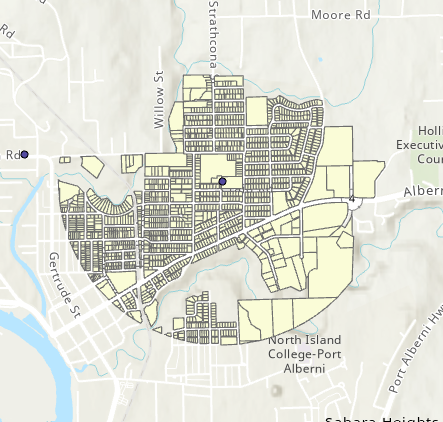
Clip
Use the Clip tool to cut one layer down to the boundaries of another.
- Works like a cookie cutter.
- Useful when we want to focus on a study area.
- Input layer: our data layer
- Clip layer: the study area
Erase
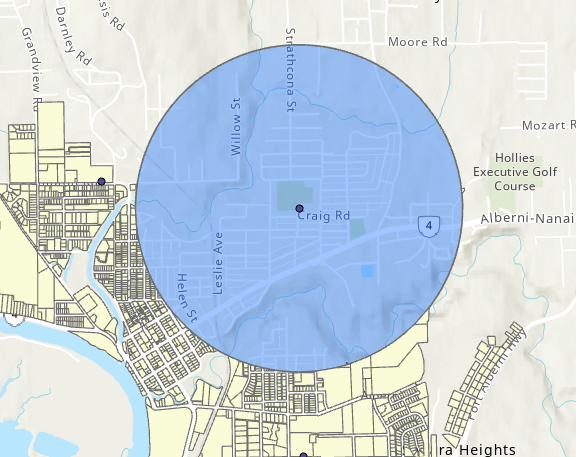
Use the erase tool to remove the area of one layer from another.
- Opposite of the clip tool.
- Useful when we want to discard/exclude an area.

Intersect
Intersect lets us see only where layers overlap and combine overlapping attributes.
- Can handle more than two layers at once.
- Splits features by overlaps and merges attribute tables.
- Useful when we want to merge and parse data at the same time.

Union
Use the Union tool to combine multiple layers, split features where they overlap and combine attributes.
- Similar to intersect, but keeps overlapping areas
- Adds attributes from all overlaps.
- Can handle more than two layers at once.
- Null values where for new attributes where no overlaps are present.
- Useful when we want to merge layers.
Many More
There are many more vector overlay tools! I have presented some of the the most frequenly used tools, but if you have specific use cases you may need others. I can't cover them all, and I don't want to overwhelm folks.