Raster Data
A simple, storage intensive format best suited for continuous fields.
Raster Data Model
Represents space continuously:
- Rectangular grid of equally sized cells
- Each cell only has one value
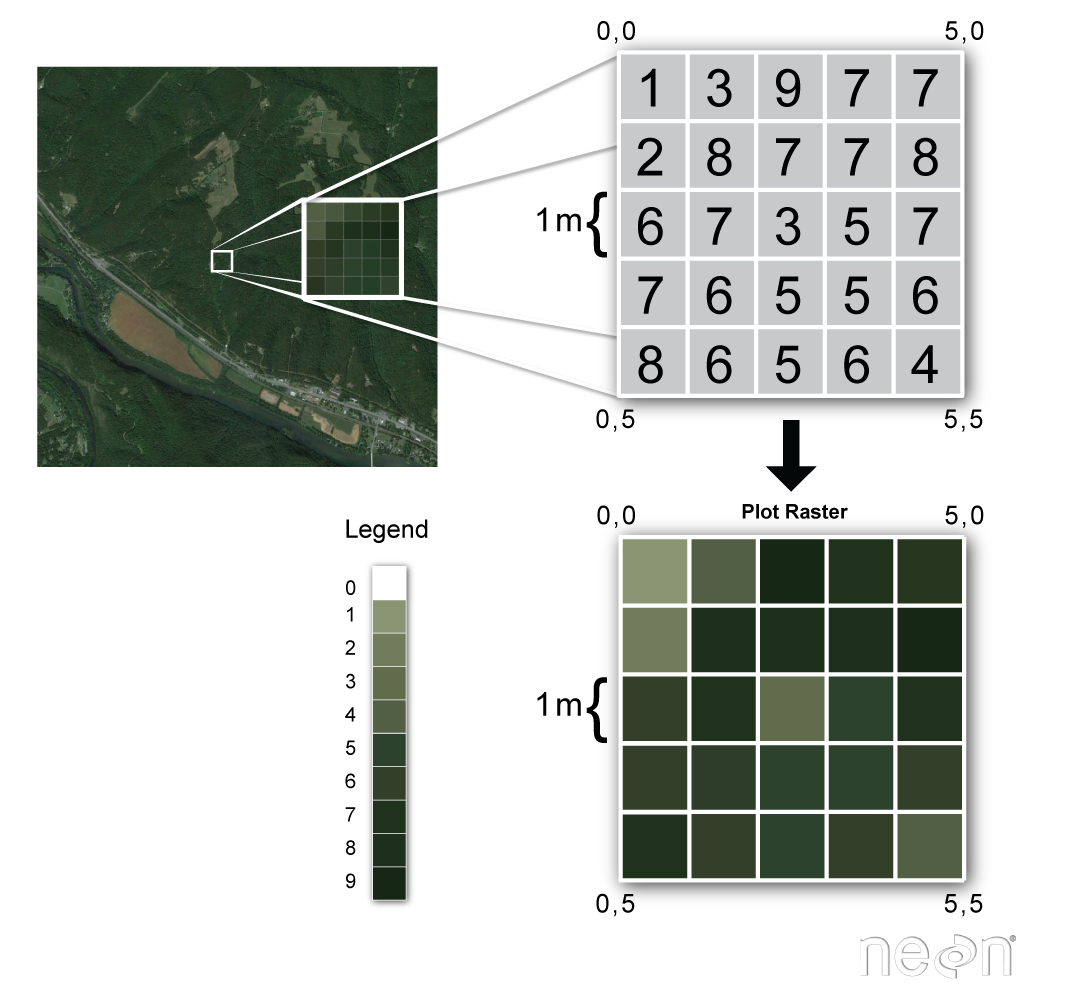
Raster Data Model
Multiple attributes, require multiple bands
- Standard color photos have three bands:
- Red, green, & blue
- LANDSAT8 has 11 bands:
- "False Color Images"
- Spectral Indicies (NDVI)
Resolution & Extent
Resolution: cell size.
- 1 m x 1 m = 1 m2
Extent: depends on number of cells.
- 5 rows, 5 columns
- 1 m cell size
- Covers 5 m x 5 m

Resolution & Extent
Resolution: 10 m cell size = 100 m2
Extent: varies with number of cells.
| Rows | Columns | Extent |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | 50 m x 50 m |
| 5 | 10 | 50 m x 100 m |
| 100 | 100 | 1 km x 1 km |
Implications
Loss of information during rasterization.
- A "bigger" issue for larger cells.
- At a certain point features become unrecognizable.
- Higher resolution = larger file for equivalent areas.
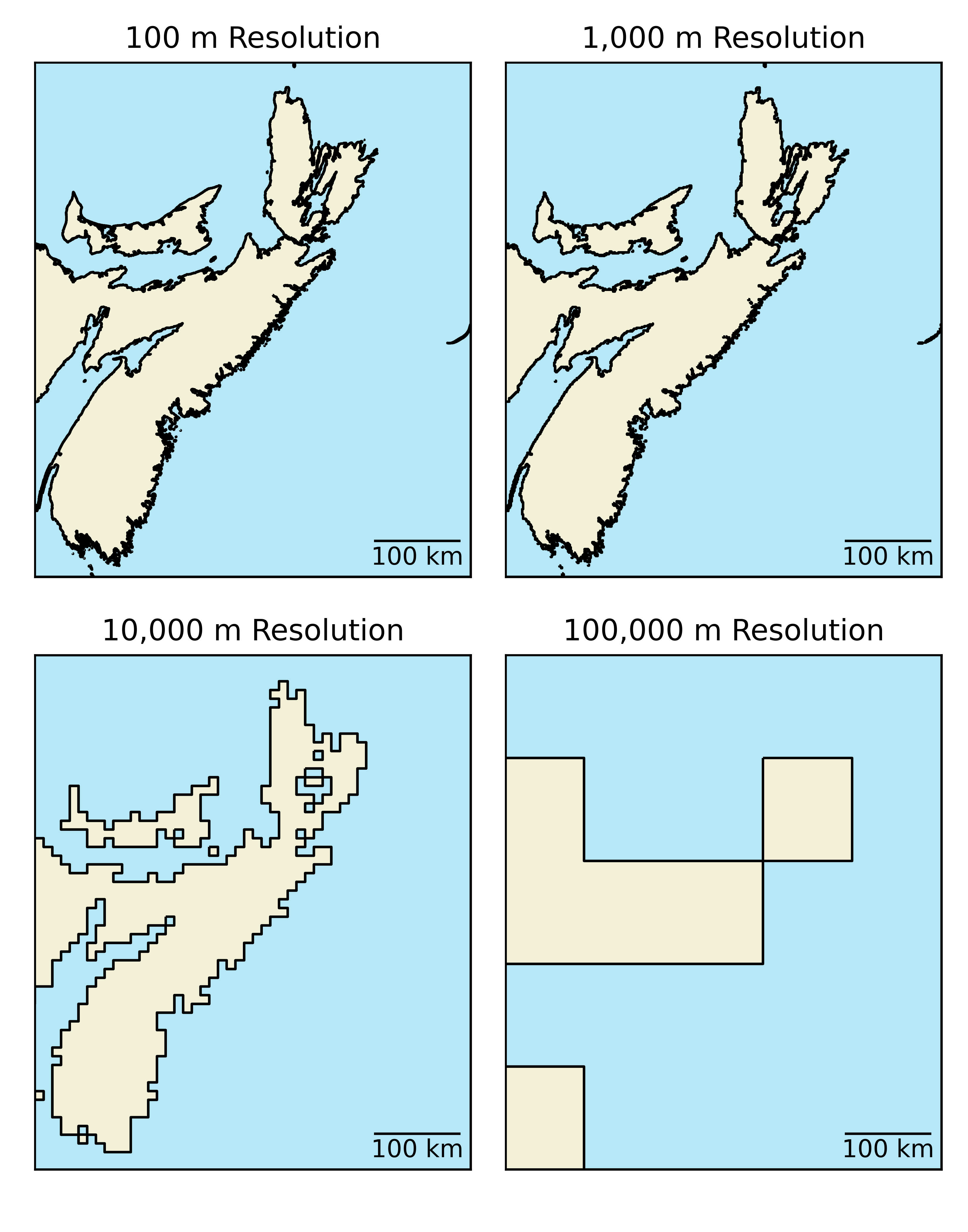
Mixed Pixel Problem
One cell: one value
- What if it covers multiple values?
- A: Winner take all
- B: Cell center
- Other options?
File Size
The number of cells per image dictates file size:
Cells = rows x columns x bands.
| Extent | Bands | Cell Size | Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 x 1 km | 1 | 100 m | 100 cells |
| 1 x 1 km | 1 | 1 m | 1,000,000 cells | 1 x 1 km | 3 | 100 m | 300 cells |
| 1 x 1 km | 3 | 1 m | 3,000,000 cells |
File Size
Increases exponentially with resolution and linearly with number of bands.
| Extent | Bands | Cell Size | Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 x 1 km | 1 | 100 m | 100 cells |
| 1 x 1 km | 1 | 1 m | 1,000,000 cells | 1 x 1 km | 3 | 100 m | 300 cells |
| 1 x 1 km | 3 | 1 m | 3,000,000 cells |
Why does this matter?
Downloading a decade (87,600 bands) of snow cover data:
- 5 min for the orange area
- 2 hrs for the red area (17x larger)
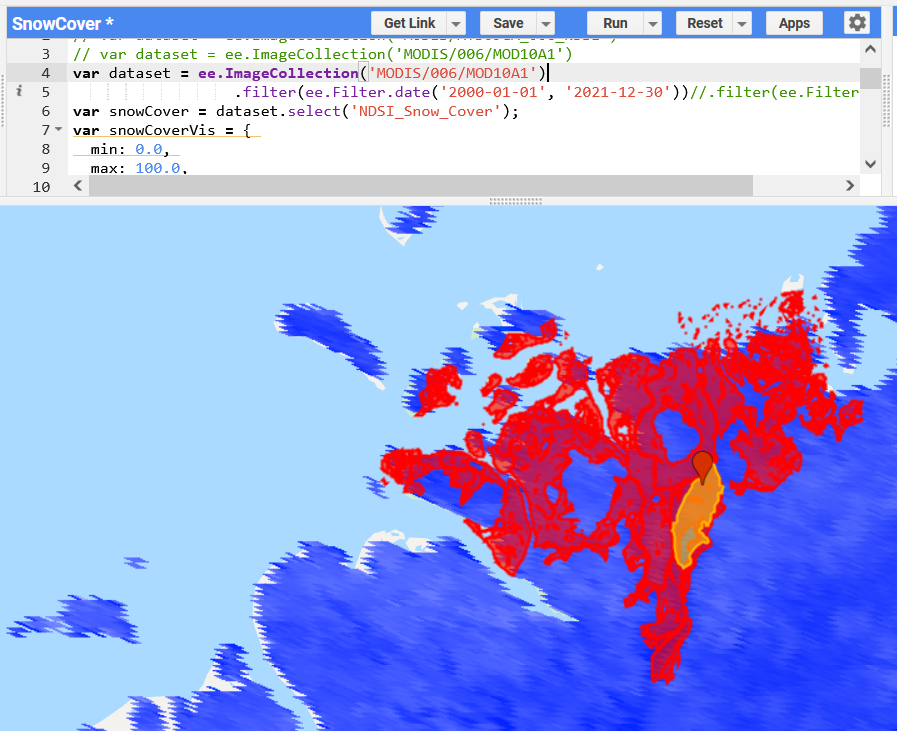
Why does this matter?
Processing times will increase as well:
- Any manipulation or analysis of the orange area will be much faster than the red area

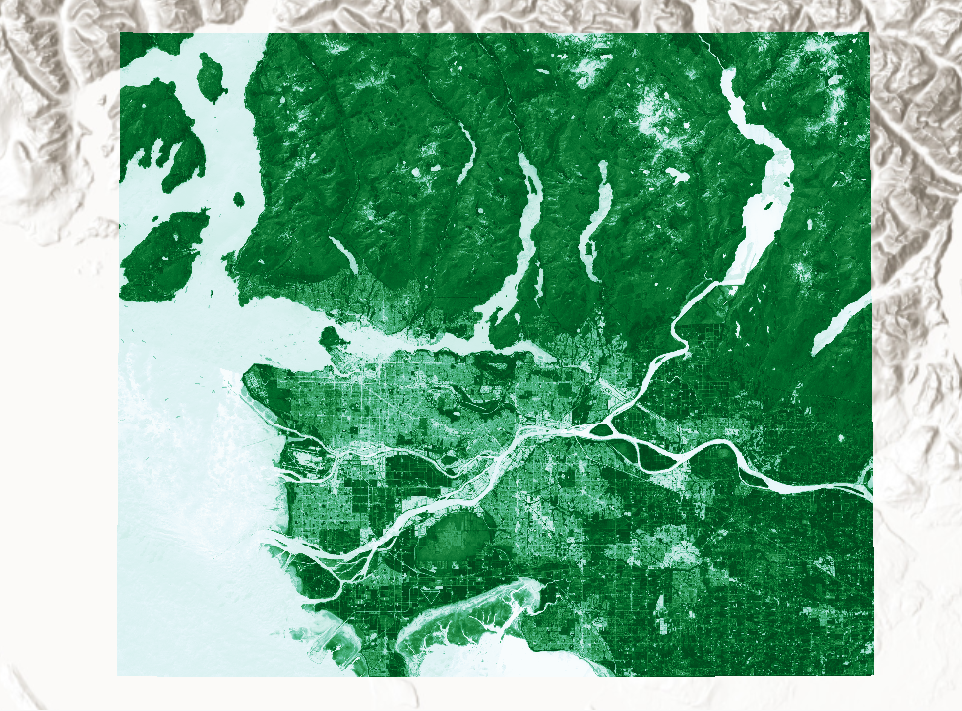
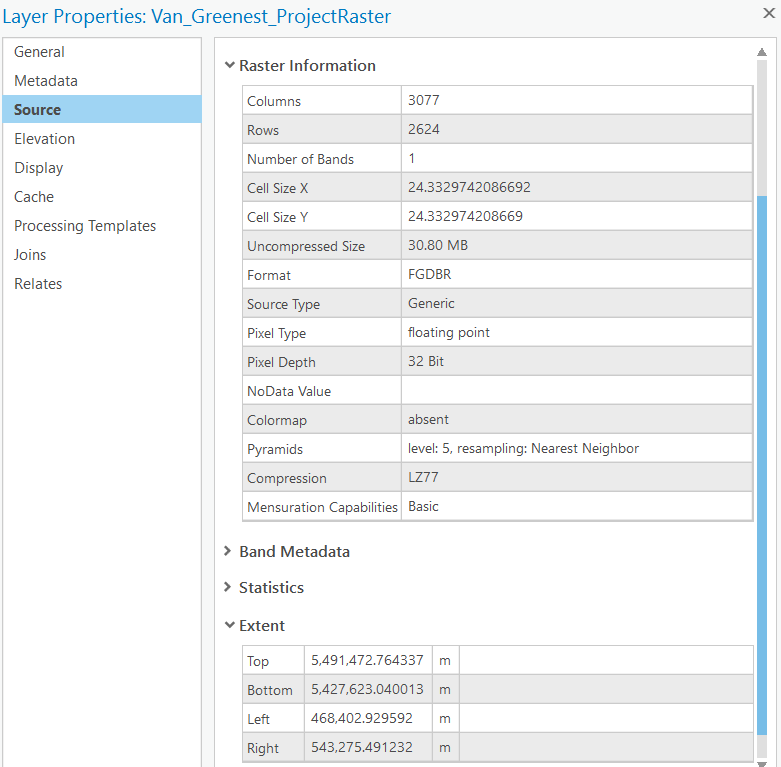
Metadata in ArcPro
Raster Overlay
A key advantage of raster data model is how algebraic expressions can be performed efficiently.
- A: Winter Temperature
- B: Summer Temperature
- Range: B-A
- Average: (A+B)/2
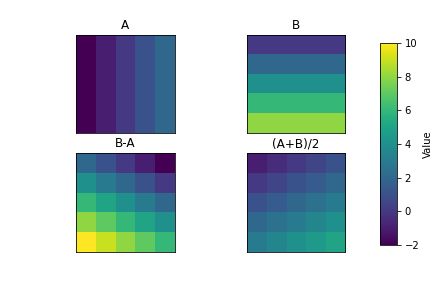
Key Advantages
- Well suited for continuous phenomena:
- Continuous in space and time.
- Simple data structure makes overlay is easy and efficient.
GeoTIFF
One of the most common/functional raster formats, based of the Tag Image File Format (TIFF). A TIFF file stores metadata (data about the data) as tags. A GeoTIFF is a standard .tif image format plus additional tags spatial tags denoting spatial information including:
- Extent (minimum x,y and maximum x,y)
- Resolution (cell size)
- Projection, Coordinate system, and datum
Other file types
Raster data can come in many different formats. You will likely encounter when working with raster data include: